How Sleep Affects Your Mental Health: The Crucial Link Between Sleep and Emotional Well-Being
Article Summary:
-
Explore the strong connection between sleep and mental health.
-
Discuss how poor sleep contributes to mental health disorders like depression, anxiety, and stress.
-
Provide tips for improving sleep to support mental well-being.
Article Content:
-
Introduction
-
Sleep and mental health are deeply interconnected. While poor mental health can interfere with sleep, inadequate sleep can also significantly affect your emotional well-being. The relationship between sleep and mental health is cyclical—one affects the other in a continuous loop. Understanding this connection is crucial for managing mental health and promoting better sleep.
In this article, we will explore how sleep impacts your mental health, why sleep deprivation is linked to mood disorders, and strategies you can use to improve sleep and enhance your emotional well-being.
-
-
The Connection Between Sleep and Mental Health
-
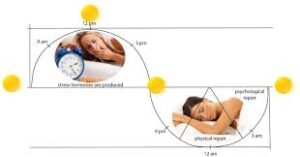
Sleep as a Regulator of Mood: Sleep is essential for regulating emotions and mood. When you sleep, your brain processes emotions, consolidates memories, and repairs neural pathways. The deeper stages of sleep (such as deep sleep and REM sleep) are particularly important for processing emotional experiences and enhancing cognitive function. Sleep deprivation disrupts this process, making it harder to cope with stress, anxiety, and negative emotions.
-
How Poor Sleep Affects Your Mental State: Sleep deprivation can lead to increased irritability, heightened emotional responses, and difficulty managing stress. It can also reduce your ability to think clearly, impair decision-making, and increase the risk of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Long-term sleep deprivation has been linked to impaired emotional regulation, making it harder to bounce back from negative experiences or manage difficult emotions.
-
-
The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Mental Health
-
Increased Risk of Depression: Chronic sleep deprivation is one of the most significant risk factors for developing depression. Studies show that individuals who get less than six hours of sleep per night are at a higher risk of developing depressive symptoms. Sleep deprivation can affect brain regions that regulate mood and emotional responses, contributing to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low energy.
-
Impact on Depression: Without proper rest, your brain becomes less effective at managing negative emotions, and the lack of sleep can exacerbate existing depressive symptoms.
-
-
Anxiety and Sleep Disturbances: Sleep and anxiety are also closely connected. People who suffer from anxiety often experience disrupted sleep, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. In turn, poor sleep can worsen feelings of anxiety, creating a vicious cycle. When you don’t get enough sleep, your ability to cope with stress and worry is reduced, and feelings of anxiety are more pronounced.
-
Impact on Anxiety: Poor sleep heightens the body's stress response, increasing the production of cortisol, the stress hormone. This can make you feel more anxious and on edge, especially when facing stressful situations.
-
-
-
How Sleep Enhances Emotional Resilience
-
Regulating Stress: A good night’s sleep plays an essential role in regulating your body’s stress response. Sleep helps to lower cortisol levels and replenish energy reserves, which are crucial for managing stress. With proper rest, you are better equipped to handle daily stressors, which in turn improves emotional resilience.
-
Mood Improvement: Sleep helps balance the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and overall feelings of well-being. When you sleep, your body restores these chemical balances, which can improve mood and reduce feelings of depression and anxiety.
-
Cognitive Benefits: Sleep also supports cognitive function, including memory, concentration, and decision-making, which are all crucial for maintaining mental health. Lack of sleep impairs your ability to think clearly and make rational decisions, which can lead to frustration and increased stress.
-
-
Tips for Improving Sleep to Support Mental Health
-
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Your sleep environment can greatly impact the quality of your rest. Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine to block out distractions. Keep your bedroom a calm and relaxing space dedicated to rest.
-
Tip: Avoid watching TV or working in bed. Use your bedroom only for sleep and intimacy to help create a mental association between the space and relaxation.
-
-
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock and circadian rhythm. This consistency improves sleep quality, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed.
-
Tip: Set a bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include activities like reading, stretching, or taking a warm bath.
-
-
Limit Stimulants: Stimulants like caffeine, nicotine, and sugar can interfere with sleep by increasing alertness and affecting the nervous system. Avoid these substances, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
-
Tip: Try switching to caffeine-free herbal teas like chamomile or peppermint in the evening, which have calming effects.
-
-
Incorporate Relaxation Techniques: To calm your mind before bed, try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation. These practices reduce stress and help you unwind, making it easier to fall asleep.
-
Tip: Try the 4-7-8 breathing technique: Inhale for 4 seconds, hold your breath for 7 seconds, and exhale slowly for 8 seconds. Repeat this cycle 4-5 times to calm your nervous system.
-
-
Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity improves sleep quality and reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety. Exercise helps release endorphins, the body’s natural stress relievers. However, avoid intense exercise right before bed, as it can increase energy and make it difficult to relax.
-
Tip: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week, but try to finish exercising a few hours before bedtime to avoid overstimulation.
-
-
-
Natural Supplements for Sleep and Mental Health
-
Melatonin: Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles. Supplementing with melatonin can be helpful for people who have difficulty falling asleep due to stress or anxiety. It is particularly useful for individuals with disrupted circadian rhythms, such as those who work night shifts or suffer from jet lag.
-
Tip: Take melatonin 30 minutes to an hour before bed, starting with a low dose and increasing if necessary.
-
-
Lavender: Lavender is well known for its calming effects on the body and mind. Studies have shown that lavender can improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety, making it an excellent natural remedy for stress-related sleep disturbances.
-
How to Use: Use lavender essential oil in a diffuser, or place a few drops on your pillow or sheets before bed. You can also take lavender supplements for additional benefits.
-
-
CBD: CBD (cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound from the cannabis plant that has gained popularity for its ability to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. It has been shown to improve sleep quality, reduce stress, and help with anxiety and depression.
-
How to Use: Try CBD oil or CBD capsules before bed, starting with a low dose and adjusting as needed.
-
-
-
When to Seek Professional Help
-
While sleep problems can often be addressed with lifestyle changes and natural remedies, persistent insomnia or mental health issues such as chronic anxiety or depression may require professional intervention. If sleep problems are affecting your quality of life or contributing to mental health issues, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a proven treatment that can help break the cycle of poor sleep and improve emotional well-being. Speaking with a therapist can also help identify and address underlying mental health issues like anxiety or depression.
-
-
Conclusion
-
Sleep is fundamental to mental health. A good night’s sleep helps regulate mood, improve emotional resilience, and support overall cognitive function. When we don’t get enough sleep, we are more susceptible to stress, anxiety, and depression, which in turn further disrupt our sleep. Improving sleep quality is a crucial step in improving mental health and emotional well-being.
By following the tips in this article—such as establishing a consistent sleep routine, incorporating relaxation techniques, and using natural remedies like melatonin and lavender—you can enhance both your sleep and your mental health. Remember, making sleep a priority is a key component of living a healthy, balanced life.
-